1 CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing 100190, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
In recent years, two-dimensional (2D) materials have attracted extensive interests due to the large exciton binding energy different from bulk materials. Many peculiar properties have been discovered that have far-reaching perspectives in the next generation of optoelectronic devices. In this review, we introduce the forms of exciton existence in 2D materials and several promising 2D materials with good applications at first. Then, we summarize relevant contemporary tools for probing exciton dynamics and methods of regulating 2D exciton transport, for instance, electrical regulation, stress/surface wave regulation and moiré potential regulation, etc. Finally, we conclude the general development of regulation in 2D materials and propose several possible opportunities of application prospect.In recent years, two-dimensional (2D) materials have attracted extensive interests due to the large exciton binding energy different from bulk materials. Many peculiar properties have been discovered that have far-reaching perspectives in the next generation of optoelectronic devices. In this review, we introduce the forms of exciton existence in 2D materials and several promising 2D materials with good applications at first. Then, we summarize relevant contemporary tools for probing exciton dynamics and methods of regulating 2D exciton transport, for instance, electrical regulation, stress/surface wave regulation and moiré potential regulation, etc. Finally, we conclude the general development of regulation in 2D materials and propose several possible opportunities of application prospect.
materials exciton diffusion transition metal dichalcogenide van deer Waals heterostructure trion moiré exciton

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing 100190, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
In recent years, one-dimensional (1D) nanomaterials have raised researcher's interest because of their unique structural characteristic to generate and confine the optical signal and their promising prospects in photonic applications. In this review, we summarized the recent research advances on the spectroscopy and carrier dynamics of 1D nanostructures. First, the condensation and propagation of exciton–polaritons in nanowires (NWs) are introduced. Second, we discussed the properties of 1D photonic crystal (PC) and applications in photonic–plasmonic structures. Third, the observation of topological edge states in 1D topological structures is introduced. Finally, the perspective on the potential opportunities and remaining challenges of 1D nanomaterials is proposed.In recent years, one-dimensional (1D) nanomaterials have raised researcher's interest because of their unique structural characteristic to generate and confine the optical signal and their promising prospects in photonic applications. In this review, we summarized the recent research advances on the spectroscopy and carrier dynamics of 1D nanostructures. First, the condensation and propagation of exciton–polaritons in nanowires (NWs) are introduced. Second, we discussed the properties of 1D photonic crystal (PC) and applications in photonic–plasmonic structures. Third, the observation of topological edge states in 1D topological structures is introduced. Finally, the perspective on the potential opportunities and remaining challenges of 1D nanomaterials is proposed.
Journal of Semiconductors
2022, 43(12): 121201
1 中国科学院纳米标准与检测重点实验室 中国科学院纳米科学卓越创新中心 国家纳米科学中心,北京 100190
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 北京大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100871
当激子与腔光子间的相互作用强于激子和腔光子的衰减时,激子能级与腔模之间产生强耦合,形成的准粒子被称为激子极化激元。激子极化激元有效质量小,同时具有较强的非线性,在慢光和低功耗发光器件等方面具有巨大的应用前景。传统Ⅲ-Ⅴ族无机半导体材料激子束缚能较弱,而有机半导体材料非线性系数较小等问题限制着室温条件下激子极化激元的应用。卤化物钙钛矿材料具有高吸收系数、长扩散长度、高缺陷容忍度以及低非辐射复合率等一系列优异的光电性质,并且具有高的激子束缚能和振子强度,成为研究光与物质强相互作用的理想材料。文中从卤化物钙钛矿结构和法布里-珀罗(Fabry-Pérot, F-P)微腔类型两方面介绍了近年来卤化物钙钛矿与F-P微腔强耦合在激子极化激元方面的研究进展。首先回顾了极化激元的研究背景和卤化物钙钛矿的基本光电特性,其次介绍了三维钙钛矿和二维层状钙钛矿各自的特点以及与F-P微腔强耦合的相关研究,随后对钙钛矿的自构型和非自构型F-P微腔激子极化激元的调控与相关应用进行了讨论,最后总结和展望了卤化物钙钛矿激子极化激元面临的挑战以及未来研究方向。
激子极化激元 钙钛矿 微腔 强耦合 exciton-polariton perovskite microcavity strong coupling 红外与激光工程
2021, 50(11): 20210619
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing 100190, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
4 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
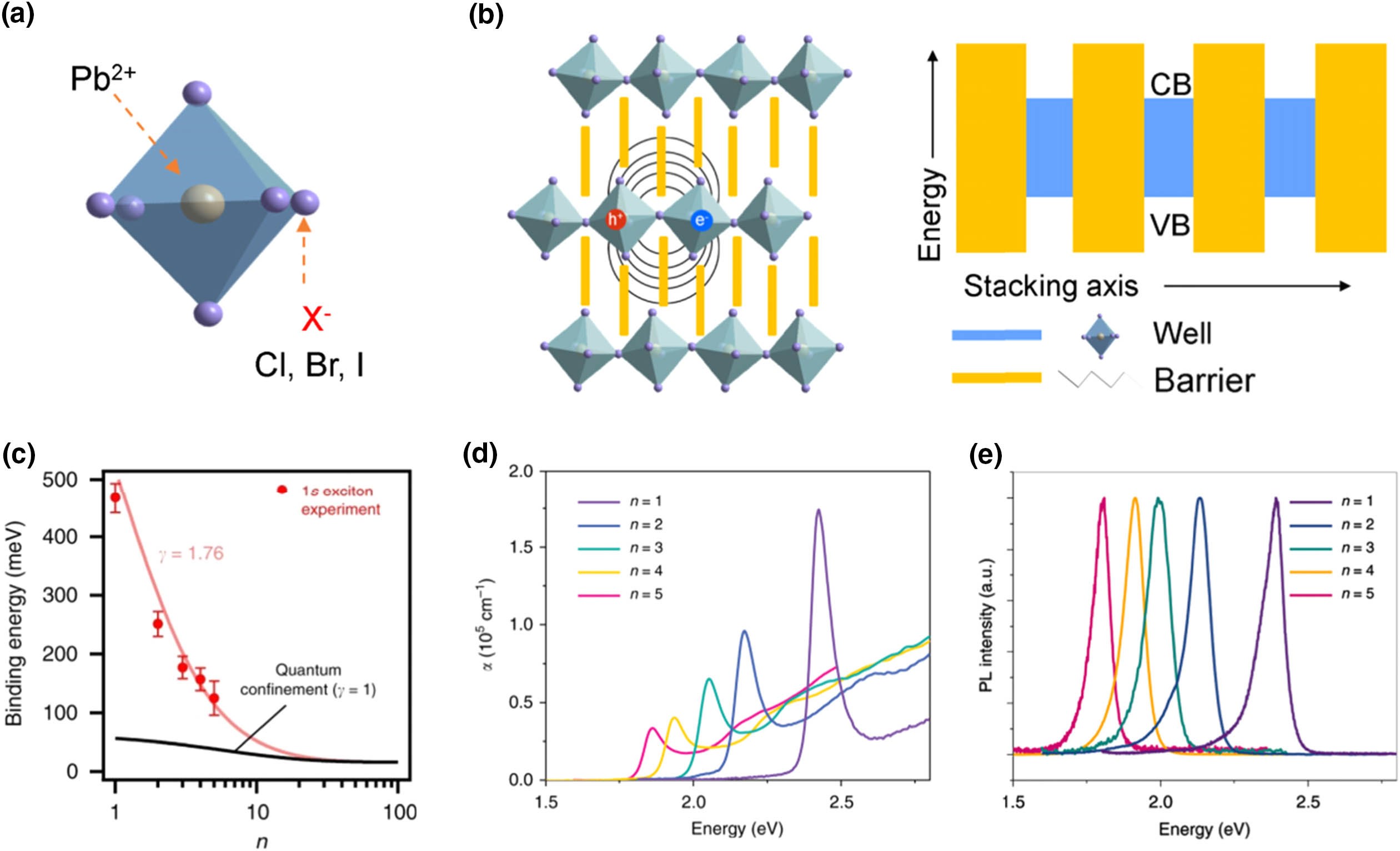
Two-dimensional (2D) perovskites are hybrid layered materials in which the inorganic lattice of an octahedron is sandwiched by organic layers. They behave as a quantum-well structure exhibiting large exciton binding energy and high emission efficiency, which is excellent for photonic applications. Hence, the cavity modulation and cavity devices of 2D perovskites are widely investigated. In this review, we summarize the rich photophysics, synthetic methods of different cavity structures, and the cavity-based applications of 2D perovskites. We highlight the strong exciton–photon coupling and photonic lasing obtained in different cavity structures. In addition, functional optoelectronic devices using cavity structures of 2D perovskites are also reviewed.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(11): 11000A72
1 山东师范大学物理与电子科学学院, 山东 济南 250358
2 国家纳米科学中心, 中国科学院纳米科学卓越创新中心, 中国科学院纳米标准与检测重点实验室, 北京 100190
3 北京大学工学院材料科学与工程系, 北京 100871
4 北京大学宽禁带半导体研究中心, 北京 100871
5 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
二维过渡金属硫族化合物(TMDC)具有独特的优势,可以作为增益材料实现激光发射。TMDC材料固有的强库仑相互作用和弱的介电屏蔽效应使其具有大的激子结合能,从而有助于实现室温下稳定的激子发光,其高达6~7的折射率能够提高光约束能力,原子层表面没有悬空键,当与硅基半导体器件连接时,能够避免晶格失配。这些独特性质使其成为极具潜力的增益材料,可以与硅基微腔连接构成激光器件,原子级厚度和近红外的光谱辐射能使其与集成器件互联。本文从光学微腔的分类和激光原理,以及二维材料激光器等方面总结了近几年基于TMDC材料的激光器研究进展,并指出了当前存在的问题及展望了其发展前景。
激光器 半导体激光器 过渡金属硫族化合物(TMDC) 光学微腔 光与物质相互作用





